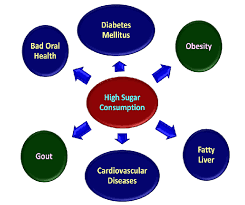
The Effects of Sugar on Health: A Comprehensive Overview
Sugar is a common ingredient found in most foods we consume daily. While it enhances the taste of many products, excessive consumption of sugar can have serious effects on our health. This article explores how sugar affects the body, the types of sugar, and practical advice on reducing sugar intake to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Understanding Sugar and Its Types
Before diving into the effects of sugar, it's essential to understand what sugar is and the different forms it takes. Sugar is a simple carbohydrate that provides energy to the body. It occurs naturally in many foods such as fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. However, the sugar added to processed foods is the one that poses the most risk to health.
Natural vs. Added Sugars
-
Natural sugars: These sugars are found naturally in whole foods. For instance, fructose in fruits and lactose in dairy products are natural sugars. The body processes these sugars more slowly because they come packaged with fiber, vitamins, and minerals, which slow down digestion.
-
Added sugars: These are sugars that are added to foods during processing. They can be found in sodas, sweets, packaged snacks, and many processed foods. Unlike natural sugars, added sugars are absorbed quickly by the body, leading to spikes in blood sugar levels.
Common Forms of Added Sugars
Some common forms of added sugars include:
- Sucrose (table sugar)
- High-fructose corn syrup (HFCS)
- Agave syrup
- Honey
- Maple syrup
- Molasses
These sugars are often included in products to enhance flavor, texture, and shelf-life, but they can contribute significantly to the overconsumption of sugar.
The Short-Term Effects of Sugar Consumption
While consuming sugar in moderation is not inherently harmful, overconsumption can lead to a variety of short-term effects on health. These effects are often immediately noticeable after indulging in sugary foods and drinks.
1. Blood Sugar Spikes
When you consume foods or drinks high in sugar, your blood glucose levels can rise rapidly. This causes the pancreas to release insulin, a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose for energy. However, in cases of excessive sugar intake, the body may not be able to keep up with the insulin demand, leading to insulin resistance over time.
The initial blood sugar spike can give you an instant boost of energy. However, this is often followed by a sharp crash, leaving you feeling sluggish, irritable, and fatigued.
2. Increased Hunger
Sugar, especially refined sugar, has been shown to stimulate appetite. It can interfere with the hormones that signal fullness, leading to overeating. This effect is partly due to sugar’s ability to raise insulin levels, which in turn promotes fat storage and reduces feelings of satiety.
3. Mood Swings
The rapid changes in blood sugar levels caused by sugary foods can also have a direct effect on your mood. After a sugar high, the sudden drop in blood sugar can lead to irritability, anxiety, and a general sense of being "off." This pattern can also increase cravings for more sugary foods, leading to a vicious cycle.
The Long-Term Health Implications of Excessive Sugar Intake
Consistently consuming high amounts of sugar can have severe long-term effects on your health. These effects often develop over time and can lead to chronic diseases.
1. Weight Gain and Obesity
One of the most well-known long-term effects of excessive sugar consumption is weight gain. Sugary foods and drinks are often high in calories but low in nutrients, which makes them easy to overconsume. Furthermore, sugar contributes to the accumulation of fat around the abdomen and liver. This type of fat, known as visceral fat, is associated with increased risk for various diseases, including cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
Sugar also disrupts normal metabolism by promoting the release of insulin, a hormone that signals the body to store fat. This makes it easier for the body to store excess fat and harder to burn it, leading to weight gain over time.
2. Increased Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
Excessive sugar intake, particularly from sugary beverages, has been closely linked to an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Over time, consuming large amounts of sugar can cause insulin resistance, which occurs when the body’s cells no longer respond effectively to insulin. This forces the pancreas to release more insulin to compensate, and eventually, the pancreas may struggle to keep up with the demand, leading to higher blood sugar levels and an increased risk of diabetes.
3. Heart Disease
Research suggests that diets high in added sugars are linked to an increased risk of heart disease. High sugar intake can lead to several risk factors for cardiovascular disease, including high blood pressure, inflammation, and elevated levels of harmful LDL cholesterol. Additionally, excess sugar can contribute to fatty liver disease, which can further affect heart health.
4. Tooth Decay
Sugar is a primary cause of tooth decay. When sugar interacts with the bacteria in the mouth, it creates acids that erode tooth enamel, leading to cavities and gum disease. The more sugar you consume, the more acid is produced, putting your oral health at risk.
5. Fatty Liver Disease
A condition known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has been closely linked to high sugar consumption. When the liver processes excess fructose (a type of sugar found in many processed foods), it can lead to fat accumulation in the liver, potentially leading to inflammation and liver damage over time.
6. Increased Risk of Certain Cancers
Some studies have suggested a correlation between excessive sugar intake and an increased risk of certain types of cancer, particularly those involving insulin resistance, such as colorectal and breast cancer. Although more research is needed in this area, it's believed that excess sugar can contribute to chronic inflammation and the growth of cancer cells.
Reducing Sugar Intake for Better Health
The key to preventing the negative effects of sugar on health lies in moderation. While it’s unrealistic to eliminate sugar entirely from your diet, reducing added sugars can go a long way in improving your health.
1. Read Food Labels Carefully
Many processed foods contain hidden sugars. Checking food labels for added sugars (often listed as "sucrose," "corn syrup," or "honey") can help you make informed choices. Ideally, your daily intake of added sugars should be limited to 25-37.5 grams (6-9 teaspoons) per day for adults, according to the American Heart Association.
2. Choose Whole Foods Over Processed Ones
Whole foods, like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, provide natural sugars and a wealth of nutrients, including fiber. When you consume whole foods, the sugar is absorbed more slowly, and you're less likely to experience rapid blood sugar fluctuations.
3. Opt for Healthier Alternatives
If you're craving something sweet, try opting for natural sweeteners like stevia or monk fruit. These alternatives have little to no effect on blood sugar levels. Additionally, eating fruits like berries or apples can provide natural sweetness along with fiber and antioxidants.
4. Drink Water Instead of Sugary Beverages
Sugary beverages like soda, fruit juices, and energy drinks are among the largest sources of added sugars in the modern diet. Drinking water, herbal teas, or sparkling water with a splash of lemon can help keep your sugar intake under control.
Conclusion
While sugar is not inherently harmful, excessive consumption can have a significant impact on your health. From weight gain and obesity to increased risk of chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers, the long-term effects of excessive sugar intake are undeniable. By being mindful of your sugar consumption and making healthier food choices, you can reduce the risk of these health issues and enjoy a better quality of life.
href="https://blogger.https://slickquiver.com/kpy542ijrm?key=374ad52b1da5daf69e0cea67de52cbfc.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgALakgAk3Ig4dbc7m7hHaYzgTJEaMieWRfLHdzj7E1JWokrsoqFn-TO1t6HAuQrd7WSLHOp-n-DVvrXt_0iLK-6Ahu1fKDyHVgppF3BykbgKb-M_-F37tuocJIvBdGWeYhKWM0r8ZjK_79escRdu2QaQo64eq35Jv2Hr5Gb9ky99RGy9mNV4QnrOZ4g7G4/s355/download.jpg" style="margin-left: 1em; margin-right: 1em;" target="_blank">